
Cataract surgery has come a long way since its inception, with significant advancements in technology and surgical techniques. As the world population continues to age, the prevalence of cataracts is increasing, creating a pressing need for innovative approaches to improve patient outcomes and quality of life. In this blog, we will explore the future of cataract surgery and the exciting developments that are on the horizon.
- Laser-Assisted Cataract Surgery
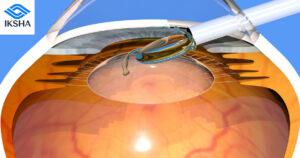
Laser-assisted cataract surgery (LACS) has already gained popularity in recent years and is expected to become even more prevalent in the future. LACS utilizes femtosecond lasers to perform key steps of the cataract surgery, such as corneal incisions, anterior capsulotomy, and lens fragmentation. This technology offers precise and reproducible results, potentially reducing complications and improving refractive outcomes. As the technology evolves, we can anticipate advancements in laser systems, further enhancing the safety and efficacy of cataract surgery.
- Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
Artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics are revolutionizing various fields of medicine, and cataract surgery is no exception. AI algorithms can assist in preoperative planning, predicting intraoperative complications, and postoperative management. By analyzing patient data and surgical outcomes, AI can help surgeons make informed decisions and personalize treatment plans for optimal results. Additionally, robotic systems may become more prominent, aiding surgeons in performing delicate maneuvers with enhanced precision and stability, ultimately improving surgical outcomes and patient safety.

- Advanced Intraocular Lenses
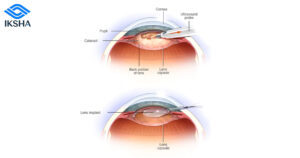
Intraocular lenses (IOLs) are artificial lenses implanted during cataract surgery to replace the clouded natural lens. Currently, monofocal IOLs are the most commonly used, providing good distance vision but often requiring glasses for near tasks. However, advanced multifocal and accommodating IOLs are emerging as exciting alternatives. Multifocal IOLs offer patients the potential for clear vision at various distances, reducing the need for glasses. Accommodating IOLs are designed to mimic the eye’s natural focusing mechanism, allowing for improved near and distance vision. As research and development progress, we can expect more sophisticated IOL designs that optimize vision quality and patient satisfaction.
- Non-Invasive Treatment Options
While cataract surgery is highly effective, some individuals may not be suitable candidates due to certain medical conditions or advanced age. Therefore, the development of non-invasive treatment options for cataracts is an area of active research. Non-surgical interventions, such as pharmacological agents or targeted therapies, may slow down or prevent cataract progression, delaying or even eliminating the need for surgery. Although these treatments are still in the experimental stages, they hold great promise for the future, potentially providing alternatives to surgical intervention.
- Enhanced Postoperative Recovery
Postoperative recovery after cataract surgery has already improved significantly, with most patients experiencing minimal discomfort and quick visual rehabilitation. However, ongoing efforts are focused on further enhancing postoperative recovery. This includes the development of new medications and technologies to reduce inflammation, accelerate corneal wound healing, and optimize visual outcomes. Additionally, telemedicine and remote monitoring systems may play a crucial role in postoperative care, allowing patients to receive follow-up consultations and monitoring from the comfort of their homes.
The Future of Cataract Surgery:
The future of cataract surgery is filled with exciting prospects, driven by advancements in technology, surgical techniques, and medical research. Laser-assisted cataract surgery, AI-assisted decision-making, and robotic systems will likely become more prevalent, improving surgical precision and patient outcomes. Advanced intraocular lenses offer the potential for personalized vision correction, while non-invasive treatments may provide alternatives to surgery. Enhanced postoperative recovery strategies and remote monitoring systems will further optimize patient care and convenience.
As the field of ophthalmology continues to advance, collaboration between surgeons, engineers, and researchers will be crucial in pushing the boundaries of cataract surgery. Clinical trials and long-term studies will help validate the safety and efficacy of emerging technologies and techniques, ensuring that patients receive the best possible care.
However, it’s important to note that with any technological advancements, there may be challenges and ethical considerations to address. Affordability and accessibility of these innovative treatments should be a priority to ensure that all patients, regardless of their economic background, can benefit from these advancements.
In conclusion, the future of cataract surgery is promising, with ongoing developments that aim to improve patient outcomes, enhance visual quality, and streamline the surgical process. Laser-assisted surgery, artificial intelligence, advanced intraocular lenses, non-invasive treatments, and enhanced postoperative recovery strategies are just a glimpse of what’s on the horizon. By embracing these advancements and fostering collaboration, we can look forward to a future where cataract surgery becomes even more precise, personalized, and patient-centric, ultimately improving the quality of life for millions of individuals worldwide.




